vLLM Workshop at MLOps Community Agent World: Hands-On Learning with Cast.ai
Introduction: My Journey with LLMs
As the GenAI wildfire spread across private organizations during my time at Education First in late 2022, I found myself captivated by developments from frontier labs. The impressive progress of the GPT model family drew me to OpenAI early on, where I prototyped various LLM-based applications by connecting to frontier models through paid API access.
At the time, skeptics dismissed “wrapper companies” as unsustainable. However, as model intelligence continued scaling while API costs decreased, a clear truth emerged: if you build a product that solves genuine customer pain points, you have both a viable business and a defensible moat.
Early Experiments: From APIs to Local Hosting
The Text-to-SQL Era
During ChatGPT 3.5’s early stages, we prototyped text-to-SQL solutions (perhaps worth a standalone post). It was a painful process of prompt engineering and hoping for the best when LLMs ran in production. The industry quickly shifted from “vibes” to rigorous evaluations, though we were admittedly still in the vibes camp.
When GPT’s multimodal capabilities emerged, I experimented with two projects:
- TikTok video analysis - Understanding viral videos to extract underlying scripts and SOPs across different geographic locations
- Shoe defect detection - Identifying manufacturing faults from product photos
Random projects, I know, but they were invaluable learning experiences with the APIs.
Local LLM Hosting Adventures
When llama.cpp and Ollama gained traction, I experimented with hosting 7B models on my MacBook. While it was thrilling to witness the Metal GPU humming away and feel the momentum of the open-source community, the models lacked the intelligence for practical applications.
The one exception: we gained access to a beefy Mac machine running LLama 70B. I attempted using it for coding questions but quickly pivoted back to ChatGPT or Claude, admitting defeat.
Why This Workshop Matters
The Open Source LLM Renaissance
Where does the open-source community stand now? Models like DeepSeek apparently surpass frontier closed models on certain benchmarks—perhaps the time has finally arrived. Simultaneously, my company is exploring the possibility of hosting our own models for cost optimization and data privacy.
This workshop, hosted by Cast.ai at the MLOps Community Agent World event, presented the perfect opportunity to acquire hands-on skills for hosting open-source LLMs via vLLM on Kubernetes.
About Cast.ai
Cast.ai is a Kubernetes automation platform that optimizes cloud costs and improves performance through intelligent resource management. Their platform is particularly well-suited for AI/ML workloads, making them an ideal partner for this vLLM workshop. Cast.ai helps organizations automatically optimize their Kubernetes clusters, which is crucial when running expensive GPU workloads for LLM inference.
 Cast.ai’s Kubernetes optimization platform - perfect for managing GPU-intensive LLM workloads
Cast.ai’s Kubernetes optimization platform - perfect for managing GPU-intensive LLM workloads
Key Takeaways from the vLLM Workshop
 vLLM: The high-performance inference engine for large language models
vLLM: The high-performance inference engine for large language models
1. vLLM: The Framework of Choice for Open Source LLM Hosting
vLLM has emerged as the de facto framework for hosting open-source LLMs, delivering optimal performance in both throughput and latency depending on specific use cases. Its sophisticated memory management and request batching make it ideal for production deployments.
2. Hardware Planning is Critical
Successful LLM deployment requires extensive upfront planning to determine the right hardware configuration and model size for your use case. Consider these scenarios:
Enterprise Chatbot Use Case:
- Expected load: 1000s of concurrent users
- Priority: Low latency for responsive user experience
- Hardware needs: Multiple high-memory GPUs with fast interconnects
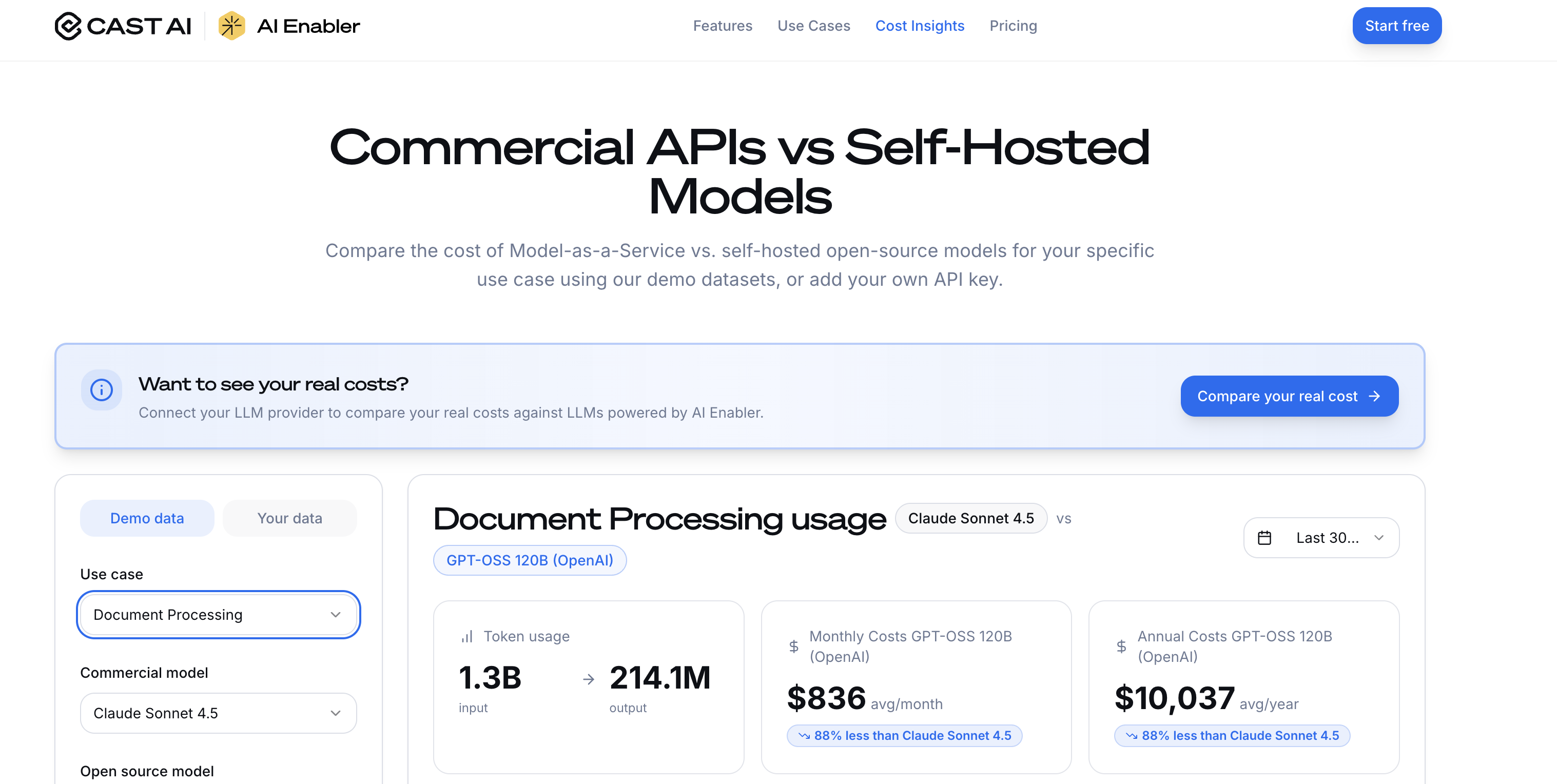
Document Processing Pipeline:
- Expected load: High token volume with batch processing
- Priority: Maximum throughput over latency
- Hardware needs: Optimized for batch sizes and memory bandwidth
The Cast.ai platform excels at this optimization challenge by automatically right-sizing your Kubernetes clusters based on actual workload patterns, potentially saving 50-70% on cloud costs while maintaining performance.
3. GPU Math: Understanding Memory vs. Compute Bounds
One of the most valuable insights from the workshop was understanding GPU performance optimization. The instructor shared a practical trick:
Calculate the Ops-per-Byte Ratio:
- High ratio → GPU is compute-bound → Increase batch size
- Low ratio → GPU is memory-bound → Decrease batch size
For any GPU card, you can estimate the optimal ops-per-byte ratio:
Optimal ratio = Compute bandwidth (FLOPS) / Memory bandwidth (bytes/sec)
This calculation helps you understand whether you’re bottlenecked by computation or memory access, allowing you to tune your deployment accordingly.
4. Deep Dive into KV Cache Mechanics
We engaged in extensive whiteboarding exercises, calculating KV cache operations and computational requirements. This hands-on approach proved invaluable for understanding:
- The underlying mechanisms of attention mechanisms
- How quantization affects KV cache size and performance
- Trade-offs between memory usage and model accuracy
- Batch processing strategies for optimal GPU utilization
It felt like being back in school—but with immediate practical applications!
5. Understanding vLLM Architecture
We explored vLLM’s architecture and request flow in depth. The pre-read assignment from this excellent article provided essential context. Key architectural components include:
- PagedAttention mechanism for efficient memory management
- Continuous batching for maximizing throughput
- Request scheduling algorithms for balancing latency and efficiency
- KV cache optimization strategies for handling large context windows
Workshop Experience and Cast.ai Integration
While we unfortunately didn’t get hands-on time deploying models on Cast.ai’s EKS cluster as originally planned, the theoretical foundation and architectural insights more than compensated. The workshop demonstrated how Cast.ai’s platform would streamline the deployment process by:
- Automatic GPU node provisioning based on model requirements
- Cost optimization through intelligent resource scheduling
- Multi-cloud support for flexibility and redundancy
- Real-time monitoring and autoscaling for LLM workloads
Understanding the integration between vLLM’s inference capabilities and Cast.ai’s Kubernetes optimization creates a powerful combination for production LLM deployments.
Next Steps: Putting Knowledge into Practice
Now armed with this knowledge, I’m planning to:
- Benchmark different model sizes on various GPU configurations
- Implement vLLM in a production environment using Kubernetes
- Explore Cast.ai’s platform for cost-optimized GPU cluster management
- Document performance metrics comparing throughput vs. latency trade-offs
- Share detailed implementation guides once deployed
Why This Matters for Your Organization
If your company is considering hosting open-source LLMs, here’s what this workshop taught me:
Cost Optimization: Using platforms like Cast.ai can dramatically reduce infrastructure costs while maintaining performance. For GPU-intensive workloads, this can mean the difference between a viable and prohibitively expensive solution.
Performance at Scale: vLLM’s architecture, combined with proper Kubernetes orchestration, enables production-grade LLM serving that can compete with managed API services in terms of latency and throughput.
Control and Privacy: Hosting your own models provides data sovereignty and customization opportunities that closed APIs cannot match.
Resources and Further Reading
- vLLM Documentation
- Aleksa Gordić’s vLLM Deep Dive (excellent pre-read)
- Cast.ai Platform - Kubernetes cost optimization for AI workloads
- Cast.ai Blog: GPU Optimization - Best practices for GPU workload management
Conclusion
This workshop reinforced that the open-source LLM ecosystem has matured significantly. With frameworks like vLLM and platforms like Cast.ai handling the infrastructure complexity, hosting your own models has become increasingly practical for organizations of all sizes.
The combination of cost optimization, performance, and control makes self-hosted LLMs a compelling alternative to API-based solutions—especially for use cases with high volume, sensitive data, or specific latency requirements.
Once I implement vLLM in production and integrate with Cast.ai’s platform, I’ll share detailed performance metrics, cost analysis, and practical deployment patterns.